Topic: Stars
Stars
Which star type has a surface temperature of4000 K and a luminosity 1000 times greater than
the Sun?
(1) dwarf
(2) main sequence
(3) giant
(4) supergiant
Which star is cooler and less luminous than the Sun?
(1) Proxima Centauri
(2) Pollux
(3) Rigel
(4) 40 Eridani B
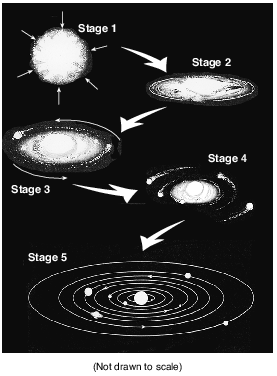
Which force was mostly responsible for the contraction of the gas cloud?
(1) friction
(2) gravity
(3) magnetism
(4) inertia

During which stage of development does the star have a cool surface temperature and the greatest luminosity?
(1) protostar
(2) main sequence
(3) giant
(4) white dwarf

The Sun is inferred to spend the greatest amount of time in its life cycle
(1) contracting from a gas cloud (nebula)
(2) as a main sequence star
(3) moving away from the main sequence and becoming a giant star
(4) changing from a giant star to a white dwarf star
The photograph below shows a feature of the universe as seen through a telescope.

This feature is best identified as
(1) a galaxy
(2) a comet
(3) an asteroid
(4) a star


Which process represented in the model is occurring in each layer of this star to produce the new chemical elements?
(1) contact metamorphism
(2) internal crystallization
(3) nuclear fusion
(4) radioactive decay
The diagram below represents a model of the size of the Sun and indicates the color of the Sun.

Which diagram best represents the relative size and indicates the color of Polaris compared to the Sun?
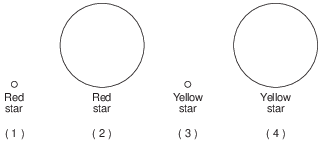
(1) 1
(2) 2
(3) 3
(4) 4
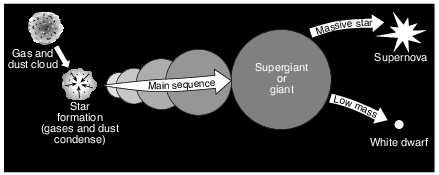
What causes the gas and dust cloud to condense and become a star?
(1) density
(2) friction
(3) gravity
(4) outgassing
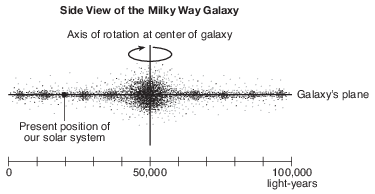
What is the distance, in light-years, from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy to our solar system? [1]
light-years
Allow 1 credit for any value from 25,000 light-years to 35,000 light-years.
The star Canopus has a surface temperature of 7400 K and a luminosity (relative to the Sun) of 1413. In your answer booklet, use an X to plot the position of Canopus on the graph, based on its surface temperature and luminosity. [1]
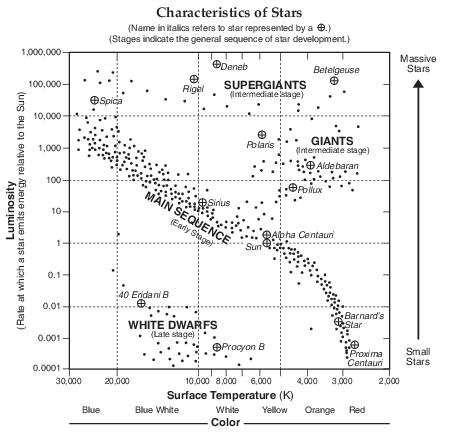
Allow 1 credit if the center of the X is placed within or touches the box shown below.
• Note: Allow credit if a symbol other than an X is used.
• It is recommended that an overlay of the same scale as the student answer booklet be used to ensure reliability in rating.
• 

Identify the nuclear process that combines lighter elements into heavier elements to produce the energy radiated by stars. [1]
Allow 1 credit for fusion or nuclear fusion.
Globular Star Clusters
Globular star clusters appear as small, hazy spots among the other stars. These clusters are groups of hundreds of thousands of stars held together by gravity. Individual stars within a cluster can be seen by using powerful telescopes, allowing scientists to determine their luminosities and temperatures.
All of the stars in a given cluster formed at the same time. In young clusters, most of the stars are classified as main sequence stars. As the stars in a cluster age, they eventually use up their core hydrogen and expand, changing from main sequence stars to giants. The most massive main sequence stars become supergiants. The less massive a star is in the cluster, the longer it remains a main sequence star. Over time, the number of main sequence stars in a cluster decreases.

Compared to the relative amount of time that star A remains in the main sequence, state how the relative amount of time that star C remains in the main sequence is different. Explain why this amount of time is different. [1]
Relative time for star C: Explanation:
Allow 1 credit if both responses are correct. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
• Relative time for star C:
• — stays in main sequence longer
• — greater amount of time/more time
• — Star A leaves the main sequence sooner.
• Explanation:
• — Star C is less massive/smaller.
• — It is cooler.
• — Star C uses up its core hydrogen more slowly.
• — Star A is more massive/larger.
• — The less massive a star is in the cluster, the longer it remains a main sequence star.
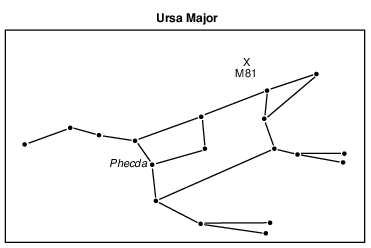

Phecda has a surface temperature of approximately 9500 K and a luminosity of 63. Identify the name of the star found on the Characteristics of Stars chart in the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ Earth Science that has a surface temperature and luminosity closest to Phecda. [1]
Allow 1 credit for Sirius.
Kepler-11 is one of many star systems discovered by space satellites. Scientists find this system unusual because of its small size and its six planets, identified by letters b through g, that orbit relatively close to its central star. The central star, Kepler-11, has a surface temperature of 5663 K and a luminosity of 1.0.

Identify the star located on the Characteristics of Stars graph on the Physical Setting/Earth Science Reference Tables that has the most similar surface temperature and luminosity as the Kepler-11 star. [1]
Allow 1 credit for the Sun.
